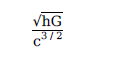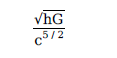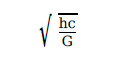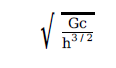Welcome Dear Student and Shine in NEET with Shine NEET SmartPrep!.
All NEET - 2016 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe
All NEET - 2016 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Limited-Time Offer: Get all this for just ₹1199
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe Now & Take Control of Your NEET Prep !
Subscribe
Your Full Test Performance Summary
Questions Available: 54
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
1. Planck’s constant (h), speed of light in vacuum (c) and Newton’sgravitational constant (G) are three fundamental constants. Which ofthe following combinations of these has the dimension of length ?
2. If the velocity of a particle is v = At + Bt2 , where A and B are constants,then the distance travelled by it between 1 s and 2 s is
3. Two cars P and Q start from a poin t at the same time in a straight line and their positions are represented by xp(t) = (at + bt2) and xQ(t) = (f t − t2) At what time do the cars have the same velocity ?
4. If the magnitude of sum of two vectors is equal to the magnitude of difference of the two vectors, the angle between these vectors is:
5. A particle moves so that its position vector is given by \(\vec{r}\) = cos wt\(\hat{x}\) + sin wt\(\hat{y}\), where w is a constant. Which of the following is true ?
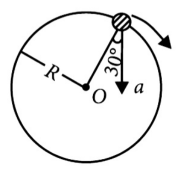
6. In the given figure, a = 15m\( s^{−2} \) represents the total acceleration of a particle moving in the clockwise direction in a circle of radius R = 2.5 m at a given instant of time. The speed of the particle is

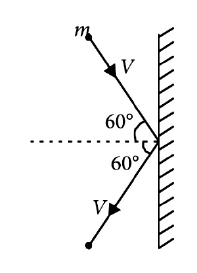
7. A rigid ball of mass m strikes a rigid w all at 60° and gets reflected without loss of speed as shown in the figure. The value of impulse imparted by the wall on the ball will be

8. A car is negotiating a curved road of radius R. The road is banked at anangle θ. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is μs. The maximum safe velocity on this road is
9. A particle of mass 10 g moves along a circle of radius 6.4 cm with a constant tangential acceleration. What is the magnitude of this acceleration if the kinetic energy of the particle becomes equal to 8 × 10−4J by the end of the second revolution after the beginning of the motion ?
10. A body of mass 1 kg begins to move under the action of time dependent force \(\vec{F}\) = \(\left(2t\hat{i} + 3t^2\hat{j}\right)\) N , where \(\hat{i}\) and \(\hat{j}\) are unit vectors along x and y axis.What power will developed by the force at the time t?
11. What is the minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter avertical loop of radius R so that can complete the loop?
12. A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally with a velocity of 400ms−1strikes a wood block of mass 2 kg which is suspended by light inextensible string of length 5 m. As a result, the centre of gravity of the block found to rise a vertical distance of 10 cm. The speed of the bullet after it emerges out horizontally from the block will be
13. Two identical balls A and B having velocities of 0.5ms−1 and 0.3ms−1 respectively collide elastically in one dimension. The velocities of B and A after the collision respectively will be
14. A particle moves from a point \(−2\hat{i} + 5\hat{j}\) to \(4\hat{j} + 3\hat{k}\) when a force of \(4\hat{i} + 3\hat{j}\) N is applied.How much work has been done by force ?
15. Two rotating bodies A and B of masses m and 2m with moments of inertia IA and IB (IB > I A) have a equal kinetic energy of rotation. If LA and LB be their angular momentum respectively, then
16. A solid sphere of mass m and radius R is rotating about its diameter. A solid cylinder of the same mass and same radius is also rotating about its geometrical axis with an angular speed twice that of the sphere. The ratio of their kinetic energies of rotation \(\frac{E_{sphere}}{E_{cylinder}}\) will be
17. A light rod of length l has two masses m1 and m2 attached to its two ends. The moment of inertia of the system about an axis perpendicular to the rod and passing through the centre of mass is
18. A disk and a sphere of same radius but different masses roll off on two inclined planes of the same altitude and length. Which one of the two objects gets to the bottom of the plane first?
19. From a disc of radius R and mass M, a circular hole of diameter R, whose rim passes through the centre is cut. What is the moment of inertia of the remaining part of the disc about a perpendicular axis, passing through the centre?
20. A uniform circular disc of radius 50 cm at rest is free to turn about an axis which is perpendicular to its plane and passes through its centre. It is subjected to a torque which produces a constant angular acceleration of 2.0 rad s−2. Its net acceleration in s−2 at the end of 2.0 S is approximately
21. Coefficient of linear expansion of brass and steel rods are \(\alpha_1\) and \(\alpha_2\). Length of brass and steel rods are \(l_1\) and \(l_2\) respectively. If \(\left(l_2 − l_1\right)\) is maintained same at all temperatures, which one of the following relations holds good?
22. A piece of ice falls from a height h so that it melts completely. Only one-quarter of the heat produced is absorbed by the ice and all energy of ice gets converted into heat during its fall. The value of \(h\) is [Latent heat of ice is \(3.4 × 10^5 J/kg\) and \(g = 10 N/kg\)
23. A black body is at a temperature of \(5760 K\). The energy of radiation emitted by the body at wavelength \(250 nm\) is \(U_1\),at wavelength \(500 nm\) is \(U_2\) and that at \(1000 nm\) is \(U_3\) Wien's constant, \(b = 2.88 × 10^6nmK\) . Which of the following is correct?
24. Two non-mixing liquids of densities \(p\) and \(np \left(n > 1\right)\) are put in a container. The height of each liquid is \(A\). A solid cylinder of length \(L\) and density \(d\) is put in this container. The cylinder floats with its axis vertical and length \(pL \left(p < 1\right)\) in the denser liquid. The density \(d\) is equal to
25. A rectangular film of liquid is extended from \(\left(4 cm × 2 cm\right)\) to \(\left(5 cm × 4 cm\right)\). If the work done is \(3 × 10^{−4}J\), the value of the surface tension of the liquid is
26. Three liquids of densities \(\rho_1\), \(\rho_2\) and \(\rho_3\) (with \(\rho_1 > \rho_2 > \rho_3\)),having the same value of surface tension \(T\), rise to the same height in three identical capillaries. The angles of contact \(θ_1\),\( θ_2\) and \(θ_3\) obey
27. Two identical bodies are made of a material for which the heat capacityincreases with temperature. One of these is at \(100^\circ C\), while the other one is at \(0^\circ C\). If the two bodies are brought into contact, then,assuming no heat loss, the final common temperature is
28. A body cools from a temperature \(3T\) to \(2T\) in \(10\) minutes. The room temperature is \(T\). Assume that Newton’s law of cooling is applicable.The temperature of the body at the end of next \(10\) minutes will be
29. A body of mass m is attached to the lower end of a spring whose upperend is fixed. The spring has negligible mass. When the mass m is slightly pulled down and released, it oscillates with a time period of \(3\, s\). When the mass m is increased by \(1\, kg\), the time period of oscillationsbecomes \(5\, s\). The value of \(m\) in kg is
30. A siren emitting a sound of frequency \(800\, Hz\) moves away from an observer towards a cliff at a speed of 15\,ms^{−1}\). Then, the frequency of sound that the observer hears in the echo reflected from the cliff is (Take velocity of sound in air = \(330ms^{−1}\))
31. An air column, closed at one end and open at the other, resonates with a tuning fork when the smallest length of the column is \(50\, cm\). The next larger length of the column resonating with the same tuning fork is
32. A uniform rope of length \(L\) and mass \(m_1\) hangs vertically from a rigid support. A block of mass \(m_2\) is attached to the free end of the rope. A transverse pulse of wavelength \(λ_1\) is produced at the lower end of the rope. The wavelength of the pulse when it reaches the top of the rope is \(λ_2\).The ratio \(\frac{λ1}{λ2}\) is
33. The second overtone of an open organ pipe has the same frequency as the first overtone of a closed pipe \(L\) metre long. The length of the open pipe will be
34. Three sound waves of equal amplitudes have frequencies \(\left(n − 1\right)\), \(n\left(n + 1\right)\). They superimpose to give beats. The number of beats produced per second will be
35. A long straight wire of radius a carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed over its cross-section. The ratio of the magnetic fields B and B', at radial distances \(\displaystyle\frac{a}{2}\) and \(2a\) respectively, from the axis of the wire is
36. A square loop ABCD carrying a current is placed near and coplanar with a long straight conductor XY carrying a current I, the net force on the loop will be
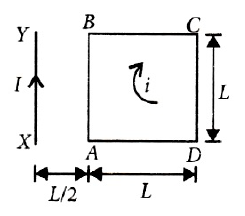

37. A long wire carrying a steady current is bent into a circular loop of one turn. The magnetic field at the centre of the loop is B. It is then bent into a circular coil of n turns. The magnetic field at the centre of this coil of n turns will be
38. An electron is moving in a circular path under the influence of a transverse magnetic field of 3.57 × 10−2T If the value of e/m is 1.76 × 1011Ckg−1, the frequency of revolution of the electron is
39. At what height from the surface of earth the gravitation potential and the value of g are \(−5.4 × 10^7J kg^{−2}\) and \(6.0ms^{−2}\) respectively? Take the radius of earth as 6400 km.
40. The ratio of escape velocity at earth (\(v_e\)) to the escape velocity at a planet (\(v_p\)) whose radius and mean density are twice as that of earth is
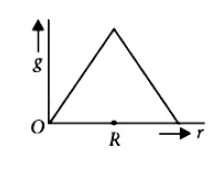
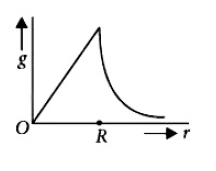
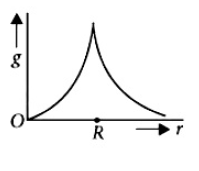
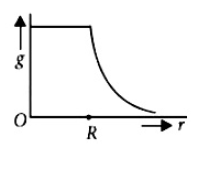
41. Starting from the centre of the earth having radius R, the variation of acceleration due to gravity is shown by
42. A satellite of mass m is orbiting the earth (of radius R) at a height h from its surface. The total energy of the satellite in terms of g0, the value of acceleration due to gravity at the earth’s surface, is
43. A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same gas is compressed separately through an adiabatic process until its volume is again reduced to half.
44. A refrigerator works between 4°C and 30°C. It is required to remove 600 calories of heat every second in order to keep the temperature of the refrigerated space constant.The power required is (Take, 1 cal =4.2Joules)
45. The temperature inside a refrigerator is \(t_2\) °C and the room temperature is \(t_1\) °C. The amount of heat delivered to the room for each joule of electrical energy consumed ideally will be
46. The molecules of a given mass of a gas have r.m.s. velocity of \(200ms^{−1}\) at \(27^\circ C\) and \(1.0 × 10^5 Nm^{ −2}\) pressure. When the temperature and pressure of the gas are respectively, \(127^ \circ C\) and 0\(.05 × 10^5 Nm^{ −2}\) , the rms velocity of itsmolecules in \(ms^{ −1}\) is
47. A given sample of an ideal gas occupies a volume V at a pressure p and absolute temperature T. The mass of each molecule of the gas is m.Which of the following gives the density of the gas?
48. One mole of an ideal monatomic gas undergoes a process described by the equation \(pV^3 = constant\). The heat capacity of the gas during this process is
49. Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two mass less strings of lengths l, are initially at a distance d (d < < l) apart because of their mutual repulsion. The charges begin to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other witha velocity v. Then, n varies as a function of the distance x between the sphere, as
50. An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity \(2 ×10^ 5 N/C\). It experiences a torque equal to 4 Nm. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
51. When ana-particle ofmass mmoving with velocity v bombardson a heavy nucleus of charge Ze, itsdistance of closest approach fromthe nucleus depends on m as
52. If an electron in a hydrogen atomjumps fromthe 3rd orbit to the 2ndorbit, it emits a photon ofwavelength l.When it jumps fromthe 4th orbit to the 3rd orbit, thecorresponding wavelength of thephoton will be
53. The half-life of a radioactive substance is 30 minutes. The time (in minutes) taken between 40% decay and 85% decay of the same radioactive substance is
54. Given the value of Rydberg constant is \(10\,\text{m}^{-1}\), the wave number of the last line of the Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum will be