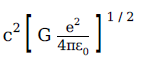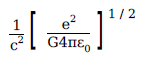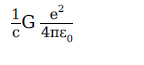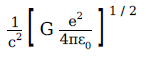Welcome Dear Student and Shine in NEET with Shine NEET SmartPrep!.
All NEET - 2017 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe
All NEET - 2017 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Limited-Time Offer: Get all this for just ₹1199
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe Now & Take Control of Your NEET Prep !
Subscribe
Your Full Test Performance Summary
Questions Available: 31
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
1. A physical quantity of the dimensions of length that can be formed out of c, G and e2/4πε0 is
[c is velocity of light, G is the universal constant of gravitation and e is charge]
[c is velocity of light, G is the universal constant of gravitation and e is charge]
2. Preeti reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator in time t1. On other days, if she remains stationary on the moving escalator, then the
escalator takes her up in time t2. The time taken by her to walk up on the moving escalator will be
3. The x and y coordinates of the particle at any time are x = 5t − 2\(t^2 \) and y = 10t respectively, where x and y are in meters and t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle at t = 2 s
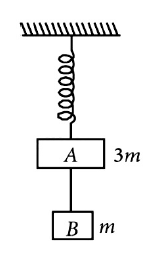
4. Two blocks A and B of masses 3m and m respectively are connected by amass-less and in extensible string. The whole system is suspended by a mass-less spring as shown in figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut are, respectively

5. One end of string of length l is connected to a particle of mass 'm' and the other end is connected to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table.If the particle moves in circle with speed 'V' , the net force on theparticle (directed towards center) will be(T represents the tension in the string)
6. Consider a drop of rain water having mass 1 g falling from a height of 1km. It hits the ground with a speed of 50ms−1. Take 'g' constant with a value 10ms−2.The work done by the (i) gravitational force and the (ii) resistive force of air is
7. A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
8. Two discs of same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2.They are brought into contact face to face coinciding the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is
9. Which of the following statements are correct?
(1) Centre of mass of a body always coincides with the centre of gravity of the body.
(2) Centre of mass of a body is the point at which the total gravitational torque on the body is zero.
(3) A couple on a body produces both transnational and rotational motion in a body.
(4) Mechanical advantage greater than one means that small effort can be used to lift a large load.
(1) Centre of mass of a body always coincides with the centre of gravity of the body.
(2) Centre of mass of a body is the point at which the total gravitational torque on the body is zero.
(3) A couple on a body produces both transnational and rotational motion in a body.
(4) Mechanical advantage greater than one means that small effort can be used to lift a large load.
10. Two rods \(A\) and \(B\) of different materials are welded together as shown infigure. Their thermal conductivities are \(K_1\) and \(K_2\) The thermal conductivity of the composite rod will be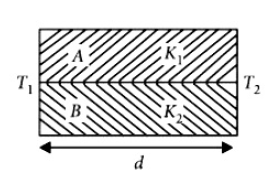

11. A spherical black body with a radius of \(12 cm\) radiates \(450 watt\) power at \(500 K\). If the radius were halved and the temperature doubled, thepower radiated in watt would be
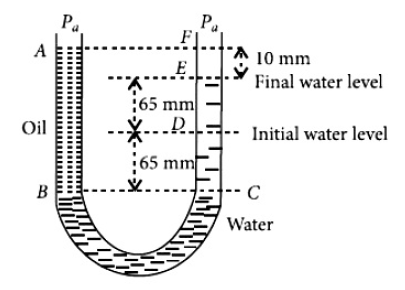
12. A U tube with both ends open to the atmosphere, is partially filled with water. Oil, which is immiscible with water, is poured into one side untilit stands at a distance of \(10 mm\) above the water level on the other side. Meanwhile the water rises by \(65 mm\) from its original level (see diagram). The density of the oil is

13. The bulk modulus of a spherical object is \('B'\). If it is subjected touniform pressure \('p'\) the fractional decrease in radius is
14. A spring of force constant k is cut into lengths of ratio \(1 : 2 : 3\). They are connected in series and the new force constant is \(k'\).Then they are connected in parallel and force constant is \(k''\).Then \(k' : k''\) is
15. A particle executes linear simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of \(3\, cm\). When the particle is at \(2\, cm\) from the mean position, the magnitude of its velocity is equal to that of its acceleration. Then its time period in seconds is
16. The two nearest harmonics of a tube closed at one end and open at other end are \(220\, Hz\) and \(260\, Hz\). What is the fundamental frequency of the system?
17. Two cars moving in opposite directions approach each other with speed of \(22\,ms^{−1}\) and \(16.5\,ms^{−1}\) respectively. The driver of the first car blows a horn having a frequency \(400\, Hz\). The frequency heard by the driver of the second car is [velocity of sound is \(340\,ms^{−1}\)]
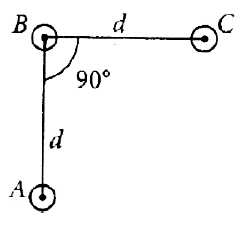
18. An arrangement of three parallel straight wires placed perpendicular to plane of paper carrying same current I along the same direction as shown in figure. Magnitude of force per unit length on the middle wire ‘B’ is given by

19. The acceleration due to gravity at a height \(1\, km\) above the earth is the same of earth. Then as at a depth \(d\) below the surface
20. Two astronauts are floating in gravitational free space after having lost contact with their spaceship. The two will
21. Thermodynamic processes are indicated in the following diagram
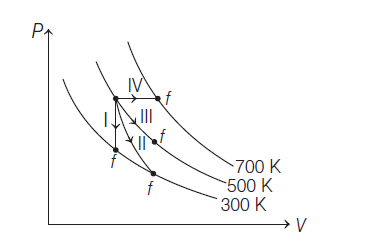
Match the following:
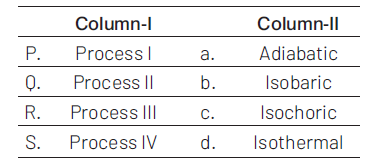

Match the following:

22. A Carnot engine having an efficiency of 110 as heat engine, is used as a refrigerator. If the workdone on the systemis 10 J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
23. A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of \(O_2\) and 4 moles of \(A_r\) at temperature T. Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is
24. Suppose the charge of a proton and an electron differ slightly. One of them is \(−e\) and the other is \(\left(e + \Delta e\right)\). If the net of electrostatic force and gravitational force between two hydrogen atoms placed at a distance d (much greater than atomic size) apart is zero, then \(\Delta e\) is of the order [Given mass of hydrogen, \(m_h =1.67 × 10^{−27} kg\)]
25. A long solenoid of diameter 0.1 m has 2 × 104 turns per metre. At the centre of the solenoid, a coil of 100 turns and radius 0.01 m is placed with its axis coinciding with the solenoid axis. The current in the solenoid reduces at a constant rate to 0 A from 4 A in 0.05 s. If the resistance of the coil is 10π2Ω, the total charge flowing through the coil during this time is
26. Figure shows a circuit that contains three identical resistors with resistance R = 9.0Ω each, two identical inductors with inductance L =2.0 mH each, and an ideal battery with emf ε = 18V . The current i through the battery just after the switch closed is
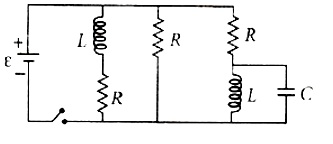

27. A capacitor is charged by a battery. The battery is removed and another identical uncharged capacitor is connected in parallel. The total electrostatic energy of resulting system
28. Suppose the charge of a proton and an electron differ slightly. One of them is -e, the other is (e+Δe). If the net of electrostatic force and gravitational force between two hydrogen atoms placed at a distance d (much greater than atomic size) apart is zero, then Δe is of the order of
[given ma of hydrogen mh = 1.67 × 10−27kg ]
[given ma of hydrogen mh = 1.67 × 10−27kg ]
29. The diagrams below show regions of equipotential. A positive charge is moved from A to B in each diagram.
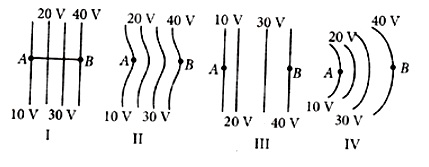

30. The ratio of wavelengths of the lastline of Balmer series and the lastline of Lyman series is
31. Radioactive material A has decay constant \(8 \lambda\) and material B has decay constant \(\lambda\). Initially, they have same number of nuclei. After what time, the ratio of number ofnuclei of material B to that A will be 1\e ?