Welcome Dear Student and Shine in NEET with Shine NEET SmartPrep!.
All NEET - 2018 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe
All NEET - 2018 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Limited-Time Offer: Get all this for just ₹1199
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe Now & Take Control of Your NEET Prep !
Subscribe
Your Full Test Performance Summary
Questions Available: 31
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
1. A student measured the diameter of a small steel ball using a screw gauge of least count 0.001 cm. The main scale reading is 5 mm and zero of circular scale division coincides with 25 divisions above the reference level. If screw gauge has a zero error of -0.004 cm, the correct diameter of the ball is
2. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
3. A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC ofinclination θ as shown in the figure.
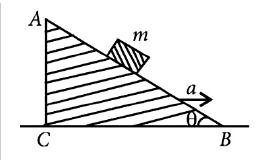
The wedge is given an acceleration a towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is

The wedge is given an acceleration a towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is
4. A moving block having mass m, collides with another stationary block having mass 4m. The lighter block comes to rest after collision. When the initial velocity of the lighter block is v, then the value of coefficientof restitution (e) will be
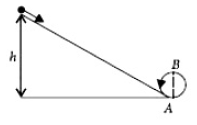
5. A body initially rest and along a frictionless track from a height h (asshown in the figure) just completes a vertical circle of diameter AB = D.The height h is equal to

6. A solid sphere is in rolling motion. In rolling motion a body possesses translational kinetic energy (Kt) as well as rotational kinetic energy(Kr) simultaneously. The ratio Kt: (Kt + K r) for the sphere is
7. A solid sphere is rotating freely about its symmetry axis in free space.The radius of the sphere is increased keeping its mass same. Which ofthe following physical quantities would remain constant for the sphere?
8. Three objects, A (a solid sphere), B (a thin circular disk) and C (acircular ring), each have the same mass M and radius R. They all spin with the same angular speed ω about their own symmetry axes. The amounts of work (W) required to bring them to rest, would satisfy the relation
9. The moment of the force, \(\vec{F} = 4\hat{i} + 5\hat{j} − 6\hat{k}\) at (2, 0, −3), about the point (2, −2, −2), is given by
10. A small sphere of radius \('r'\) falls from rest in a viscous liquid. As a result, heat is produced due to viscous force. The rate of production ofheat when the sphere attains its terminal velocity, is proportional to
11. Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume.The first wire has cross-sectional area A and the second wire has cross-sectional area 3A. If the length of the first wire is increased by \(\Delta l \) on applying a force \(F\) , how much force is needed to stretch the second wire by the same amount?
12. The power radiated by a black body is \(P\) and it radiates maximum energy at wavelength, \(\lambda_0\). If the temperature of the black body is now changed so that it radiates maximum energy at wavelength \(\frac{3}{4} \lambda_0\), the power radiated by it becomes \(n_p\). The value of n is
13. A pendulum is hung from the roof of a sufficiently high building and is moving freely to and fro like a simple harmonic oscillator. The acceleration of the bob of the pendulum is \(20ms^{−2}\) at a distance of 5mfrom the mean position. The time period of oscillation is
14. A tuning fork is used to produce resonance in a glass tube. The length of the air column in this tube can be adjusted by a variable piston. At room temperature of \(27^\circ C\) two successive resonances are produced at \(20\,cm\) and \(73\,cm\) of column length. If the frequency of the tuning fork is \(320\,Hz\), the velocity of sound in air at \(27^\circ C\) is
15. The fundamental frequency in an open organ pipe is equal to the third harmonic of a closed organ pipe. If the length of the closed organ pipe is \(20\,cm\), the length of the open organ pipe is
16. A metallic rod of mass per unit length 0.5 kgm−1 is lying horizontally on a smooth inclined plane which makes an angle of \(30^\circ\) with the horizontal. The rod is not allowed to slide down by flowing a current through it when a magnetic field of induction 0.25 T is acting on it in the vertical direction. The current flowing in the rod to keep it stationary is
17. Current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer is 5 div/mA and its voltage sensitivity (angular deflection per unit voltage applied) is 20 div/V. The resistance of the galvanometer is
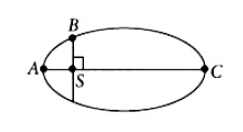
18. The kinetic energies of a planet in an elliptical orbit about the Sun, at positions \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) are \(K_A\), \(K_B\) and \(K_C\), respectively. \(AC\) is the major axis and \(SB\) is perpendicular to \(AC\) at the position of the Sun \(S\) as shown in the figure. Then

19. If the mass of the Sun were ten times smaller and the universal gravitational constant were ten times larger in magnitude, which of the following is not correct?
20. A sample of 0.1 g of water at 100°C and normal pressure (\(1.013 X 10^5 Nm^{-2}\) ) requires 54 cal of heat energy to convert to steam at 100°C. If the volume of the steam produced is 167.1 cc, the change in internal energy of the sample,
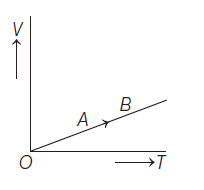
21. The volume (V) of a monoatomic gas varies with its temperature (T), as shown in the graph. The ratio of work done by the gas, to the heat absorbed by it, when it undergoes a change from state A to state B, is

22. At what temperature will the rms speed of oxygen molecules become just sufficient for escaping from the Earth’s atmosphere? (Given: mass of oxygen molecule,\(m = 2.76 × 10^−{26}\, kg\) ,Boltzmann’s constant\(k_B = 1.38 10^{-23} J K^{ −1}\))
23. An electron falls from rest through a vertical distance h in a uniform and vertically upward directed electric field E. The direction of electric field is now reversed, keeping its magnitude the same. A proton is allowed to fall from rest in it through the same vertical distance h. The time of fall of the electron, in comparison to the time of fall of the proton is
24. The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25mJ , when the current in the inductor is 60mA. This inductor is of inductance
25. An inductor 20mH , a capacitor 100μF and a resistor 50Ω are connected in series across a source of emf, V = 10 sin 314 t. The power loss in the circuit is
26. An electron falls from rest through a vertical distance h in a uniform and vertically upward directed electric field E. The direction of electricfield is now reversed, keeping its magnitude the same. A proton is allowed to fall from rest in it through the same vertical distance h. The time of fall of the electron, in comparison to the time of fall of the proton is
27. The electrostatic force between the metal plates of an isolated parallel plate capacitor C having a charge Q and area A, is
28. A toy car with charge q moves on a frictionless horizontal plane surface under the influence of a uniform electric field \(\vec{E}\). Due to the force q \(\vec{E}\), its velocity increases from 0 to 6 ms−1 in one second duration. At that instant the direction of the field is reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between 0 to 3 seconds are respectively
29. The ratio of kinetic energy to thetotal energy of an electron in aBohr orbit of the hydrogen atom, is
30. For a radioactive material, half-life is 10 minutes. If initially there are 600 number of nuclei, the time taken (in minutes) for the disintegration of 450 nuclei is
31. The efficiency of an ideal heat engine working between the freezing point and boiling point of water, is