Welcome Dear Student and Shine in NEET with Shine NEET SmartPrep!.
All NEET - 2019 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe
All NEET - 2019 questions are displayed here. But you would be able to try only a sub set of these questions in your free trial.
We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Subscribe to full version of smart test prep solution for the same cost of a static and boring printed question bank!
Limited-Time Offer: Get all this for just ₹1199
Why settle for outdated methods when you can prepare smarter, track better, and score higher?
Subscribe Now & Take Control of Your NEET Prep !
Subscribe
Your Full Test Performance Summary
Questions Available: 47
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
1. In an experiment, the percentage of error occurred in the measurement of physical quantities A, B, C and D are 1%, 2%, 3% and 4% respectively. Then the maximum percentage of error in the measurement X, where \(\displaystyle X = \frac{A^2B^{1/2}}{C^{1/3}D^3}\) will be
2. The unit of thermal conductivity is
3. The main scale of a vernier callipers has n divisions/cm. n divisions of the vernier scale coincide with (n-1) divisions of main scale. The least count of the vernier callipers is,
4. The speed of a swimmer in still water is 20m ∕ s. The speed of river water is 10m ∕ s and is flowing due east. If he is standing on the south bank and wishes to cross the river along the shortest path, the angle at which he should make his strokes w.r.t. north is, given by
5. When an object is shot from the bottom of a long smooth inclined plane kept at an angle \(60^\circ \) with horizontal, it can travel a distance \( {x_1} \) along the plane. But when the inclination is decreased to \(30^\circ \) and the same object is shot with the same velocity, it can travel \( {x_2} \) distance. Then \( {x_1}:{x_2} \) will be
6. Two particles A and B are moving in uniform circular motion in concentric circles of radii rA and rB with speed vA and vB respectively. Their time period of rotation is the same. The ratio of angular speed of A to that of B will be
7. A particle starting from rest, moves in a circle of radius r. It attains a velocity of \( {V_0 m} \) m/s in the \( {n^{th}} \) round. Its angular acceleration will be
8. A block of mass 10kg is in contact against the inner wall of a hollow cylindrical drum of radius 1m. The coefficient of friction between theblock and the inner wall of the cylinder is 0.1. The minimum angular velocity needed for the cylinder to keep the block stationary when the cylinder is vertical and rotating about its axis, will be (g = 10m ∕ s2)
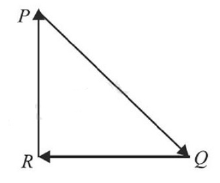
9. A particle moving with velocity \( \vec{v}\) is acted by three forces shown by the vector triangle PQR. The velocity of the particle will

10. An object flying in air with velocity \(20\hat{i} + 25\hat{j} − 12\hat{k}\) suddenly breaks in two pieces whose masses are in the ratio 1: 5 . The smaller mass flies off with a velocity \(100\hat{i} + 35\hat{j} + 8\hat{k}\) The velocity of the larger piece will be
11. Body A of mass 4m moving with speed u collides with another body B ofmass 2m, at rest. The collision is head on and elastic in nature. After the collision the fraction of energy lost by the colliding body A is
12. A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y -direction where F is in newton and y in meter. Work done by this force to move the particle from y = 0 to y = 1m is
13. A mass m is attached to a thin wire and whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break when
14. A particle of mass 5m at rest suddenly breaks on its own into three fragments. Two fragments of mass m each move along mutually perpendicular direction with speed v each. The energy released during the process is
15. A solid cylinder of mass 2kg and radius 4cm is rotating about its axis atthe rate of 3 rpm. The torque required to stop it after 2π revolutions is
16. A disc of radius 2m and mass 100kg rolls on a horizontal floor. Itscentre of mass has speed of 20cm ∕ s. How much work is needed to stopit?
17. A solid cylinder of mass 2kg and radius 50cm rolls up an inclined planeof angle inclination \(30^\circ\). The centre of mass of cylinder has speed of 4m ∕ s. The distance travelled by the cylinder on the incline surface will be (Take g = 10m ∕ s2)
18. A copper rod of 88cm and an aluminium rod of unknown length have their increase in length independent of increase in temperature. The length of aluminium rod is \(\left(\alpha_{Cu} = 1.7 × 10^{−5}K^{−1}, \alpha_{Al} = 2.2 × 10^{−5}K^{−1}\right)\)
19. A small hole of area of cross-section \(2 mm^2\) is present near the bottom ofa fully filled open tank of height \(2 m\). Taking \(g = 10 m ∕ s^2\), the rate offlow of water through the open hole would be nearly
20. When a block of mass M is suspended by a long wire of length L, thelength of the wire becomes (L + l ). The elastic potential energy storedin the extended wire is
21. A soap bubble, having radius of 1mm, is blown from a detergentsolution having a surface tension of \(2.5 × 10^{−2}N ∕ m\). The pressure inside the bubble equals at a point \(Z_0\) below the free surface of water in a container. Taking \(g = 10 m ∕ s^2\), density of water = \(10^3kg ∕ m^3\), the value of \(Z_0\) is
22. Two small spherical metal balls, having equal masses, are made from materials of densities \(\rho_1\) and \(\rho_2 \left(\rho_1 = 8\rho_2\right)\) and have radii of 1mm and2mm, respectively. They are made to fall vertically (from rest) in aviscous medium whose coefficient of viscosity equals \(\eta\) and whose density is \(0.1\rho_2\). The ratio of their terminal velocities would be
23. The stress-strain curves are drawn for two different materials X and Y .It is observed that the ultimate strength point and the fracture point areclose to each other for material X but are far apart for material Y . Wecan say that materials X and Y are likely to be (respectively)
24. The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion isgiven by \(y = A_0 + A sin ω t + B cos ω t\). Then the amplitude of its oscillation is given by
25. Average velocity of a particle executing SHM in one complete vibrationis
26. The radius of circle, the period of revolution, initial position and sense of revolution are indicated in the figure.
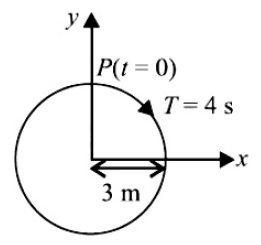
y - projection of the radius vector of rotating particle \(P\) is

y - projection of the radius vector of rotating particle \(P\) is
27. The distance covered by a particle undergoing SHM in one time periodis (amplitude = \(A\))
28. A tuning fork with frequency \(800\,Hz\) produces resonance in a resonance column tube with upper end open and lower end closed by water surface. Successive resonance are observed at length \(9.75\,cm\), \(31.25\,cm\) and \(52.75\,cm\). The speed of sound in air is
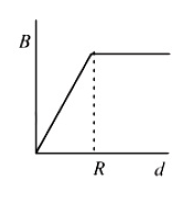
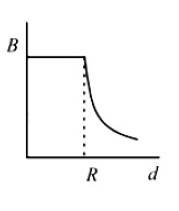
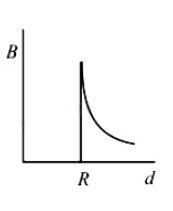
29. A cylindrical conductor of radius R is carrying a constant current. The plot of the magnitude of the magnetic field, B with the distance, d from the centre of the conductor, is correctly represented by the figure
30. Ionized hydrogen atoms and α-particles with same momenta enters perpendicular to a constant magnetic field, B. The ratio of their radii of their paths rH : rα wil be
31. Two toroids 1 and 2 have total number of turns 200 and 100 respectively with average radii 40cm and 20cm respectively. If they carry same current i, the radio of the magnetic fields along the two loops is
32. A straight conductor carrying current i splits into two parts as shown in the figure. The radius of the circular loop is R. The total magnetic fieldat the centre P at the loop is
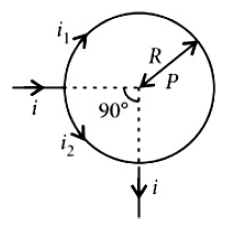

33. The work done to raise a mass \(m\) from the surface of the earth to a height \(h\), which is equal to the radius of the earth, is
34. A body weighs \(200\,N\) on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh half way down to the centre of the earth ?
35. The time period of a geostationary satellite is \(24\,h\), at a height \(6R_E\) (\(R_E\) is radius of earth) from surface of earth. The time period of another satellite whose height is \(2.5R_E\) from surface will be,
36. In which of the following processes, heat is neither absorbed nor released by a system?
37. Increase in temperature of a gas filled in a container would lead to
38. Two point charges A and B, having charges +Q and −Q respectively, are placed at certain distance apart and force acting between them is F. If 25% charge of A is transferred to B,then force between the charges becomes
39. Two parallel infinite line charges with linear charge densities \(+\lambda C/m\)and \(−\lambda C/m\) are placed at adistance of 2R in free space.What is the electric field mid-waybetween the two line charges?
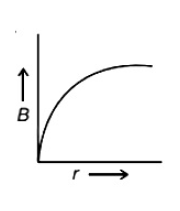
40. A hollow metal sphere of radius R is uniformly charged.The electric field due to the sphere at a distance r from the centre
41. In which of the following devices, the eddy current effect is not used?
42. A 800 turn coil of effective area 0.05m2 is kept perpendicular to amagnetic field 5 × 10−5 T. When the plane of the coil is rotated by 90∘ around any of its coplanar axis in 0.1 s, the emf induced in the coil will be
43. A hollow metal sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The electricfield due to the sphere at a distance r from the centre
44. Two point charges A and B, having charges +Q and −Q respectively, are placed at certain distance apart and force acting between them is F . If 25% charge of A is transferred to B, then force between the charges becomes
45. Two parallel infinite line charges with linear charge densities +λ C/m and -λ C/m are placed at a distance of 2R in free space. What is the electric field mid-way between the two line charges?
46. The total energy of an electron inan atomin an orbit is −3 4 . eV.Its kinetic and potential energiesare, respectively:
47. a-particle consists of