Your Performance Summary!
Questions Available: 15
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
Year: 2020 October
Topic: Electric charges and fields
1. The acceleration of an electron due to the mutual attraction between the electron and a proton when they are 1.6 Å apart is,\(\left(m_e ~ 9 ×10^{−31} kg, e =1.6 ×10^{−19} C\right)\) take, \(\left(\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon _0} = 9 x 10^9 Nm^2C^{-2}\right)\)
(1).\(10^{24} m/s^2\)
(2). \(10^{23} m/s^2\)
(3). \(10^{22} m/s^2\)
(4). \(10^{25} m/s^2\)
Solution
Year: 2019
Topic: Electric charges and fields
2. Two point charges A and B, having charges +Q and −Q respectively, are placed at certain distance apart and force acting between them is F. If 25% charge of A is transferred to B,then force between the charges becomes
(1).9F/16
(2). 16F/9
(3). 4F/3
(4). F
Solution
Year: 2017
Topic: Electric charges and fields
3. Suppose the charge of a proton and an electron differ slightly. One of them is \(−e\) and the other is \(\left(e + \Delta e\right)\). If the net of electrostatic force and gravitational force between two hydrogen atoms placed at a distance d (much greater than atomic size) apart is zero, then \(\Delta e\) is of the order [Given mass of hydrogen, \(m_h =1.67 × 10^{−27} kg\)]
(1).\(10^{-20} C\)
(2). \(10^{-23} C\)
(3). \(10^{-37} C\)
(4). \(10^{-47} C\)
Solution
Year: 2016
Topic: Electric charges and fields
4. Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two mass less strings of lengths l, are initially at a distance d (d < < l) apart because of their mutual repulsion. The charges begin to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other witha velocity v. Then, n varies as a function of the distance x between the sphere, as
(1).\(v \propto {x}\)
(2). \(v \propto {x^{-\frac{1}{2}}}\)
(3). \(v \propto {x^{-1}}\)
(4). \(v \propto {x^{\frac{1}{2}}}\)
Solution
Year: 2021
Topic: Electric charges and fields
5. A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move?
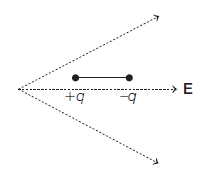

(1).Towards the left as its potential energy will increase
(2). Towards the right as its potentialenergy will decrease
(3). Towards the left as its potentialenergy will decrease
(4). Towards the right as its potentialenergy will increase
Solution
Year: 2020 September
Topic: Electric charges and fields
6. A spherical conductor of radius 10cm has a charge of \(3.2 ×10^{−7} C\) distributed uniformly.What is the magnitude of electric field at a point 15 cm from the centre of the sphere? \(\left(\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon _0} = 9×10^9 Nm^2/C^2\right)\)
(1).\(1.28×10^5 N/C\)
(2). \(1.28×10^6 N/C\)
(3). \(1.28×10^7 N/C\)
(4). \(1.28×10^4 N/C\)
Solution
Year: 2018
Topic: Electric charges and fields
7. An electron falls from rest through a vertical distance h in a uniform and vertically upward directed electric field E. The direction of electric field is now reversed, keeping its magnitude the same. A proton is allowed to fall from rest in it through the same vertical distance h. The time of fall of the electron, in comparison to the time of fall of the proton is
(1).10 times greater
(2). 5 times greater
(3). smaller
(4). equal
Solution
Year: 2021
Topic: Electric charges and fields
8. Polar molecules are the molecules
(1).having zero dipole moment
(2). acquire a dipole moment only in the presence of electric field due to displacement of charges.
(3). acquire a dipole moment only when magnetic field is absent
(4). having a permanent electric dipole moment
Solution
Year: 2020 October
Topic: Electric charges and fields
9. The electric field at a point on the equatorial plane at a distance r from the centre of a dipole having dipole moment \(\vec{P}\) is given by (r >> separation of two charges forming the dipole,\(\epsilon _0\) = permittivity of free space)
(1).\(E = \frac{P}{4\pi \epsilon _0 r^3}\)
(2). \(E = \frac{2P}{4\pi \epsilon _0 r^3}\)
(3). \(E = \frac{-P}{4\pi \epsilon _0 r^2}\)
(4). \(E = \frac{-P}{4\pi \epsilon _0 r^3}\)
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2019
Topic: Electric charges and fields
12. Two parallel infinite line charges with linear charge densities \(+\lambda C/m\)and \(−\lambda C/m\) are placed at adistance of 2R in free space.What is the electric field mid-waybetween the two line charges?
(1).\(\frac{2 \lambda}{\pi \epsilon _0 R}\) N/C
(2). \(\frac{ \lambda}{\pi \epsilon _0 R}\) N/C
(3). \(\frac{ \lambda}{2 \pi \epsilon _0 R}\) N/C
(4). Zero
Solution
Year: 2019
Topic: Electric charges and fields
13. A hollow metal sphere of radius R is uniformly charged.The electric field due to the sphere at a distance r from the centre
(1).zero as r increases for r < R,decreases as r increases for r > R
(2). zero as r increases for r < R,increases as r increases for r > R
(3). decreases as r increases for r < Rand for r > R
(4). increases as r increases for r < R and for r > R
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Electric charges and fields
14. Two identical charged conducting spheres A and B have their centres separated by a certain distance. Charge on each sphere is q and the force of repulsion between them is F. A third identical uncharged conducting sphere is brought in contact with sphere A first and then with B and finally removed from both. New force of repulsion between spehere A and B (Radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation so that for calculating force between them they can be considered as point charges) is best given as:
(1).\(\displaystyle \frac{3F}{8}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{3F}{5}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{2F}{3}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{F}{2}\)
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Electric charges and fields
15. An electric dipole with dipole moment \(5 \times 10^{-4}\) Cm is aligned with the direction of a uniform electric field of magnitude \(4 \times 10^5\) N/C. The dipole is then rotated through an angle of \(60^\circ\) with respect to the electric field. The change in the potential energy of the dipole is:
(1).1.5 J
(2). 0.8 J
(3). 1.0 J
(4). 1.2 J