Your Performance Summary!
Questions Available: 32
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
Solution
Year: 2023 Manipur
Topic: Thermodynamics
2. A container of volume \(200\, cm^3\) contains 0.2 mole of hydrogen gasand 0.3 mole of argon gas. The pressure of the system at temperature 200 K ( \(R=8.3\,JK^{−1} mol^{−1}\)) will be
(1).\(6.15 X 10^5\, pa\)
(2). \(6.15 X 10^4\, pa\)
(3). \(4.15 X 10^5\, pa\)
(4). \(4.15 X 10^6\, pa\)
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2022 Phase 2
Topic: Thermodynamics
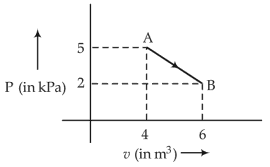
5. An ideal gas follow a process described by the equation \(PV^2 = C \) from the initial (\(P_1\), \(V_1\), \(T_1\)) to final (\(P_2\), \(V_2\), \(T_2\)) thermodynamic states, where C id a constant. Then
(1).If \(P_1\, >\, P_2\) then \(V_1\, >\, V_2\)
(2). If \(P_1\, >\, P_2\) then \(T_1\, <\, T_2\)
(3). If \(V_2\, >\, V_1\) then \(T_2\, >\, T_1\)
(4). If \(V_2\, >\, V_1\) then \(T_2\, <\, T_1\)
Solution
Year: 2022 Phase 2
Topic: Thermodynamics
6. Two rods one made of copper and other made of steel of same length and same cross-sectional area are joined together. The thermal conductivity of copper and steel are \(385\, J s^{−1} K^{−1} m^{−1}\) and \(50\, Js^{−1} K^{−1} m^{−1}\) respectively. The free ends of copper and steel are held at \(100^\circ C\) and \(0^\circ C\) respectively. The temperature at the junction is, nearly:
(1).\(88.5^\circ C\)
(2). \(12^\circ C\)
(3). \(50^\circ C\)
(4). \(73^\circ C\)
Solution
Year: 2022 Phase 2
Topic: Thermodynamics
7. Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains helium (monoatomic), the second contains fluorine (diatomic) and the third contains sulfur hexafluoride (polyatomic). The correct statement, among the following is :
(1).The root mean square of sulfur hexafluoride is the largest
(2). All vessels contain number of respective molecules
(3). The root mean square speed of molecules is same in all three cases
(4). The root mean suare speed of helium is the largest
Solution
Year: 2022
Topic: Thermodynamics
8. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state as shown in the figure below. Those processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. The curve which represents the adiabatic process among 1, 2, 3 and 4 is
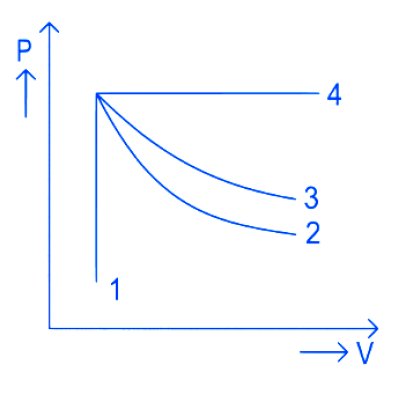

(1).1
(2). 2
(3). 3
(4). 4
Solution
Solution
Year: 2019 Odisha
Topic: Thermodynamics
10. 1g of water, of volume \(1\,cm^3\) at 100°C is converted into steam at same temperature under normal atmospheric pressure = (~\(1 × 10^5\,Pa\)). The volume of steam formed equals \(1671\,cm^3\) . If the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water is \(2256\, J/g\), the change in internal energy is
(1).2423 J
(2). 2089 J
(3). 167 J
(4). 2256 J
Solution
Year: 2018
Topic: Thermodynamics
11. A sample of 0.1 g of water at 100°C and normal pressure (\(1.013 X 10^5 Nm^{-2}\) ) requires 54 cal of heat energy to convert to steam at 100°C. If the volume of the steam produced is 167.1 cc, the change in internal energy of the sample,
(1).42.2 J
(2). 208.7 J
(3). 104.3 J
(4). 84.5 J
Solution
Solution
Year: 2020 September
Topic: Thermodynamics
13. Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stop cock. A contains an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stop cock is suddenly opened. The process is
(1).adiabatic
(2). isochoric
(3). isobaric
(4). isothermal
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2017
Topic: Thermodynamics
16. Thermodynamic processes are indicated in the following diagram
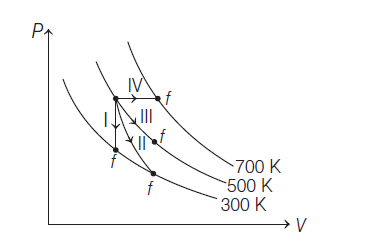
Match the following:
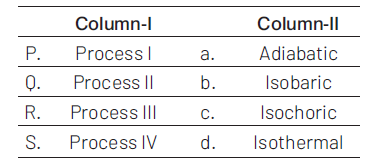

Match the following:

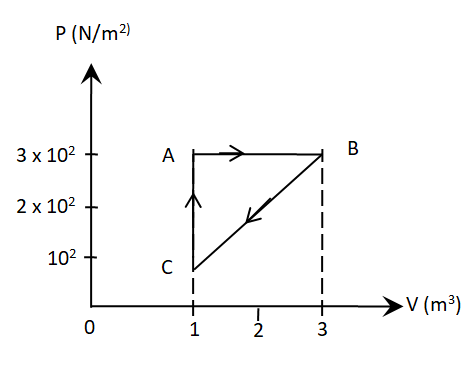
(1).\(P\rightarrow a\), \(Q\rightarrow c\), \(R\rightarrow d\), \(S\rightarrow b\)
(2). \(P\rightarrow c\), \(Q\rightarrow a\), \(R\rightarrow d\), \(S\rightarrow b\)
(3). \(P\rightarrow c\), \(Q\rightarrow d\), \(R\rightarrow b\), \(S\rightarrow a\)
(4). \(P\rightarrow d\), \(Q\rightarrow b\), \(R\rightarrow a\), \(S\rightarrow c\)
Solution
Year: 2016
Topic: Thermodynamics
17. A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same gas is compressed separately through an adiabatic process until its volume is again reduced to half.
(1).compressing the gas through adiabatic process will require more work to be done.
(2). compressing the gas isothermally or adiabatically will require the same amount of work.
(3). which of the case (whether compression through isothermal or through adiabatic process) requires more work will depend upon the atomicity of the gas.
(4). compressing the gas isothermally will require more work to be done.
Solution
Solution
Year: 2016
Topic: Thermodynamics
19. A refrigerator works between 4°C and 30°C. It is required to remove 600 calories of heat every second in order to keep the temperature of the refrigerated space constant.The power required is (Take, 1 cal =4.2Joules)
(1).23.65 W
(2). 236.5 W
(3). 2365 W
(4). 2.365 W
Solution
Year: 2016
Topic: Thermodynamics
20. The temperature inside a refrigerator is \(t_2\) °C and the room temperature is \(t_1\) °C. The amount of heat delivered to the room for each joule of electrical energy consumed ideally will be
(1).\(\frac{t_1}{t_1-t_2}\)
(2). \(\frac{t_1 + 273}{t_1-t_2}\)
(3). \(\frac{t_2 + 273}{t_1-t_2}\)
(4). \(\frac{t_1 + t_2}{t_1 + 273}\)
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2021
Topic: Thermodynamics
24. A cup of coffee cools from \(90^\circ C\) to \(80^\circ C\) in t minutes, when the room temperature is \(20^\circ C\). The time taken by a similar cup of coffee to cool from \(80^\circ C\) to \(60^\circ C\) at a room temperature same at \(20^\circ C\) is
(1).\(\displaystyle \frac{5}{13}\, t\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{13}{10}\, t\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{13}{5}\, t\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{10}{13}\, t\)
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2015
Topic: Thermodynamics
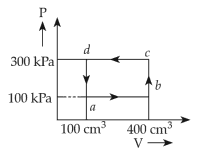
27. Figure below shows two paths that may be taken by a gas to go from a state A to a state C.
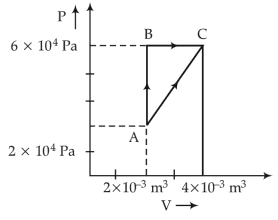
In process AB, 400 J of heat is added to the system and in process BC, 100 J of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be

In process AB, 400 J of heat is added to the system and in process BC, 100 J of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be
(1).380 J
(2). 500 J
(3). 460 J
(4). 300 J
Solution
Year: 2015
Topic: Thermodynamics
28. A carnot engine, having an efficiency of \(\displaystyle \eta\,=\,\frac{1}{10}\) as heat engine, is used as a refrigerator. If the work done on the system is 10 J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservior at lower temperature is
(1).100 J
(2). 99 J
(3). 90 J
(4). 1 J
Solution
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Thermodynamics
30. Two gases A and B are filled at the same pressure in separate cylinders with movable pistons of radius \(\text{r}_\text{A}\) and \(\text{r}_\text{B}\), respectively. On supplyig an equal amount of heat to both the systems reversibly under constant presurre, the pistons of gas A nd B are displaced by 16 cm and 9 cm, respectively. If the change in their internal energy is the same, then the ration \(\displaystyle \frac{\text{r}_\text{A}}{\text{r}_\text{B}}\) is equal to
(1).\(\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{4}{3}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{3}{4}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Thermodynamics
31. A container has two chambers of volumes \(\text{V}_1\,=\, 2\,\text{litres}\) and \(\text{V}_2\,=\, 3\,\text{litres}\) separated by a partition made of a thermal insulator. The chambers contain n1 = 5 and n2 = 4 moles of ideal gas at pressure p1 = 1 and p2 = 2 atm, respectively. When the partition is removed, the mixture attains equilibrium pressure of
(1).1.8 atm
(2). 1.3 atm
(3). 1.6 atm
(4). 1.4 atm
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Thermodynamics
32. An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressures at temperature \(27^\circ\ \text{C}\). The mass of oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to:
[Given, \(\text{R}\,=\, \frac{100}{12}\text{J mol}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) and molecular mass of \(\text{O}_2\,=\, 32\), 1 atm pressure \(=\,1.01 \times 10^5 \text{N/m}\)]
[Given, \(\text{R}\,=\, \frac{100}{12}\text{J mol}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) and molecular mass of \(\text{O}_2\,=\, 32\), 1 atm pressure \(=\,1.01 \times 10^5 \text{N/m}\)]
(1).0.156 kg
(2). 0.125 kg
(3). 0.144 kg
(4). 0.116 kg