Your Performance Summary!
Questions Available: 31
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
Year: 2024
Topic: Laws of motion
1. A box of mass 5 kg is pulled by a cord, up along a frictionless plane inclined at \(30^\circ\) with the horizontal. The tension in the cord is 30N. The acceleration of the box is (Take g = \(10 m s^{−2}\))
(1).\(2 m s^{−2}\)
(2). Zero
(3). \(0.1 m s^{−2}\)
(4). \(1 m s^{−2}\)
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2023
Topic: Laws of motion
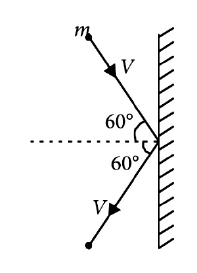
4. A 1kg object strikes a wall with velocity \(1m s^{−1}\) at an angle of \(60^\circ\) with the wall and reflects at the same angle. If it remains in contact with wall for 0.1 s, then the force exerted on the wall is :
(1).\(30\sqrt{3}\) N
(2). Zero
(3). \(10\sqrt{3}\) N
(4). \(20\sqrt{3}\) N
Solution
Solution
Year: 2023
Topic: Laws of motion
6. Calculate the maximum acceleration of a moving car so that a bodylying on the floor of the car remains stationary. The coefficient of static friction between the body and the floor is 0.15 (g = 10 \(m s^{−2})\).
(1).\( 150 m s^{−2}\)
(2). \(1.5 m s^{−2}\)
(3). \(50 m s^{−2}\)
(4). \(1.2 m s^{−2}\)
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2022
Topic: Laws of motion
9. Two bodies of mass 4kg and 6kg are tied to the ends of a massless string. The string passes over a pulley which is frictionless (see figure).The acceleration of the system in terms of acceleration due to gravity (g) is:
(1).g ∕ 2
(2). g ∕ 5
(3). g ∕ 10
(4). g
Solution
Year: 2019
Topic: Laws of motion
10. A block of mass 10kg is in contact against the inner wall of a hollow cylindrical drum of radius 1m. The coefficient of friction between theblock and the inner wall of the cylinder is 0.1. The minimum angular velocity needed for the cylinder to keep the block stationary when the cylinder is vertical and rotating about its axis, will be (g = 10m ∕ s2)
(1).\(10\pi\) rad ∕ s
(2). \(\sqrt{10}\) rad ∕ s
(3). \(102\pi \) rad ∕ s
(4). \(10\) rad ∕ s
Solution
Solution
Year: 2019
Topic: Laws of motion
12. An object flying in air with velocity \(20\hat{i} + 25\hat{j} − 12\hat{k}\) suddenly breaks in two pieces whose masses are in the ratio 1: 5 . The smaller mass flies off with a velocity \(100\hat{i} + 35\hat{j} + 8\hat{k}\) The velocity of the larger piece will be
(1).\(4\hat{i} + 23\hat{j} − 16\hat{k}\)
(2). \(−100\hat{i}− 35\hat{j}− 8\hat{k}\)
(3). \(20\hat{i}+ 15\hat{j}− 80\hat{k}\)
(4). \(−20\hat{i}− 15\hat{j} − 80\hat{k}\)
Solution
Year: 2018
Topic: Laws of motion
13. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
(1).Rolling friction is smaller than sliding friction.
(2). Limiting value of static friction is directly proportional to normalreaction.
(3). Frictional force opposes the relativemotion.
(4). Coefficient of sliding friction has dimensions of length.
Solution
Year: 2018
Topic: Laws of motion
14. A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC ofinclination θ as shown in the figure.
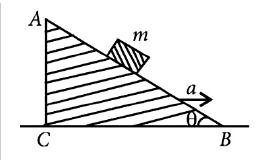
The wedge is given an acceleration a towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is

The wedge is given an acceleration a towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is
(1).\(a = \frac{g}{cosecθ}\)
(2). \(a = \frac{g}{sin θ}\)
(3). \(a = g cos θ\)
(4). \(a = g tan θ\)
Solution
Year: 2017
Topic: Laws of motion
15. Two blocks A and B of masses 3m and m respectively are connected by amass-less and in extensible string. The whole system is suspended by a mass-less spring as shown in figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut are, respectively
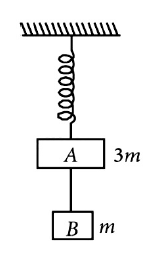

(1).\(\frac{g}{3}\), \(g\)
(2). \(g\), \(g\)
(3). \(\frac{g}{3}\), \(\frac{g}{3}\)
(4). \(g\), \(\frac{g}{3}\)
Solution
Year: 2017
Topic: Laws of motion
16. One end of string of length l is connected to a particle of mass 'm' and the other end is connected to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table.If the particle moves in circle with speed 'V' , the net force on theparticle (directed towards center) will be(T represents the tension in the string)
(1).\(T + \frac{mv^2}{l}\)
(2). \(T - \frac{mv^2}{l}\)
(3). zero
(4). \(T\)
Solution
Solution
Year: 2016
Topic: Laws of motion
18. A car is negotiating a curved road of radius R. The road is banked at anangle θ. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is μs. The maximum safe velocity on this road is
(1).\(\sqrt{\frac{g\mu_s + tanθ}{R1 − \mu_stanθ}}\)
(2). \(\sqrt{\frac{g\mu_s + tanθ}{R^21 − \mu_stanθ}}\)
(3). \(\sqrt{gR^2\frac{\mu_s + tanθ}{1 − \mu_stanθ}}\)
(4). \(\sqrt{gR\frac{\mu_s + tanθ}{1 − \mu_stanθ}}\)
Solution
Year: 2015
Topic: Laws of motion
19. Two stones of masses m and 2m are whirled in horizontal circles, theheavier one in a radius r2and the lighter one in radius r. The tangentialspeed of lighter stone is n times that of the value of heavier stone whenthey experience same centripetal forces. The value of n is
(1).4
(2). 1
(3). 2
(4). 3
Solution
Year: 2015
Topic: Laws of motion
20. A plank with a box on it at one end is gradually raised about the otherend. As the angle of inclination with the horizontal reaches 30°, the box starts to slip and slides 4.0 m down the plank in 4.0 s. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the box and the plank will be,respectively
(1).0.5 and 0.6
(2). 0.4 and 0.3
(3). 0.6 and 0.6
(4). 0.6 and 0.5
Solution
Year: 2015
Topic: Laws of motion
21. A block A of mass m1 rests on a horizontal table. A light stringconnected to it passes over a frictionless pully at the edge of table andfrom its other end another block B of mass m2 is suspended. Thecoefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is μk.When the block A is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is
(1).\(\frac{m_1m_2\left(1 +\mu_k\right)g}{\left(m_1 + m_2\right)}\)
(2). \(\frac{m_1m_2\left(1 − /mu_k\right)}{g\left(m_1 + m_2\right)}\)
(3). \(\frac{\left(m_2 + μ_km_1\right)}{g\left(m_1 + m_2\right)}\)
(4). \(\frac{\left(m_2 − μ_km_1\right)}{g\left(m_1 + m_2\right)}\)
Solution
Year: 2014
Topic: Laws of motion
22. A system consists of three masses \(m_1\), \(m_2\) and \(m_3\) connected by a string passing over a pulley P. The mass \(m_1\) hangs freely and \(m_2\) and \(m_3\) are on a rough horizontal table (the coefficient of friction = \(\mu\)).The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The downward acceleration of mass \(m_1\) is (Assume \(m_1\) = \(m_2\) = \(m_3 \) = m)
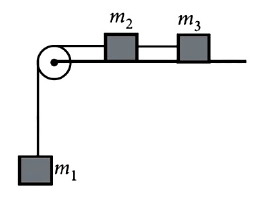

(1).\(\frac{g\left(1 − g\mu\right)}{9}\)
(2). \(\frac{2g\mu}{3}\)
(3). \(\frac{g\left(1 − 2\mu\right)}{3}\)
(4). \(\frac{g\left(1 − 2\mu\right)}{2}\)
Solution
Solution
Year: 2014
Topic: Laws of motion
24. A balloon with mass m is descending down with an acceleration a (where a < g). How much mass should be removed from it so that it starts moving up with an acceleration a?
(1).\(\frac{2ma}{g + a}\)
(2). \(\frac{2ma}{g − a}\)
(3). \(\frac{ma}{g + a}\)
(4). \(\frac{ma}{g} − a\)
Solution
Year: 2021
Topic: Laws of motion
25. A particle is released from height S from the surface of the Earth. At a certain height its kinetic energy is three times its potential energy. The height from the surface of earth and the speed of the particle at thatinstant are respectively
(1).\(\frac{S}{4}\), \(\frac{3gS}{2}\)
(2). \(\frac{S}{4}\),\(\frac{\sqrt{3gs}}{2}\)
(3). \(\frac{S}{2}\),\(\frac{\sqrt{3gs}}{2}\)
(4). \(\frac{S}{4}\),\(\sqrt{\frac{3gs}{2}}\)
Solution
Solution
Year: 2015
Topic: Laws of motion
27. A mass m moves in a circle on a smooth horizontal plane with velocity v0 at a radius R0.The mass is attached to a string which passes through a smooth hole in the plane as shown.The tension in the string is increased gradually and finally m moves in a circle of radius Ro/2.The final value of the kinetic energy is
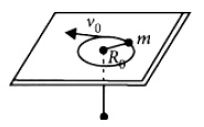

(1).\(2m{v_0}^2\)
(2). \(\frac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2 \)
(3). \(m{v_0}^2\)
(4). \(\frac{1}{4}m{v_0}^2\)
Solution
Solution
Year: 2020
Topic: Laws of motion
29. Two bodies of mass 4 kg and 6 kg are tied to the ends of a massless string. The string passes over a pulley which is frictionless (see figure). The acceleration of the system in terms of acceleration due to gravity (g) is
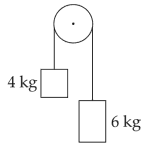

(1).\(\displaystyle \frac{g}{2}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{g}{5}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{g}{10}\)
(4). \(g\)
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Laws of motion
30. There are two inclined surfaces of equal length (L) and same angle of inclination \(45^\circ\) with the horizontal. One of them is rough and the other is perfectly smooth. A given body takes 2 times as much time to slide down on rough surface than on the smooth surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction (\(\mu_k\)) between the object and the rough surface is close to
(1).0.75
(2). 0.25
(3). 0.40
(4). 0.5
Solution
Year: 2025
Topic: Laws of motion
31. A ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from a height of 40 m. The ball hits the ground and rises to a height of 10 m. The impulse imparted to the ball during its collision with the ground is (Take \(g\, =\, 9.8 m/s^2\))
(1).84 NS
(2). 21 NS
(3). 7 NS
(4). 0